

The gain of an electron adds more electrons to the outermost shell which increases the radius because there are now more electrons further away from the nucleus and there are more electrons to pull towards the nucleus so the pull becomes slightly weaker than of the neutral atom and causes an increase in atomic radius. Figure 3: The ionic radius decreases for the generation of positive ions.Īn anion, on the other hand, will be bigger in size than that of the atom it was made from because of a gain of an electron. A neutral atom X is shown here to have a bond length of 180 pm and then the cation X + is smaller with a bond length of 100 pm. This can similarly be said about the protons pulling the electrons closer to the nucleus, which as a result decreases atomic size.įigure 3 below depicts this process. If ten magnets and ten metallic objects represent a neutral atom where the magnets are protons and the metallic objects are electrons, then removing one metallic object, which is like removing an electron, will cause the magnet to pull the metallic objects closer because of a decrease in number of the metallic objects. An analogy to this can be of a magnet and a metallic object.
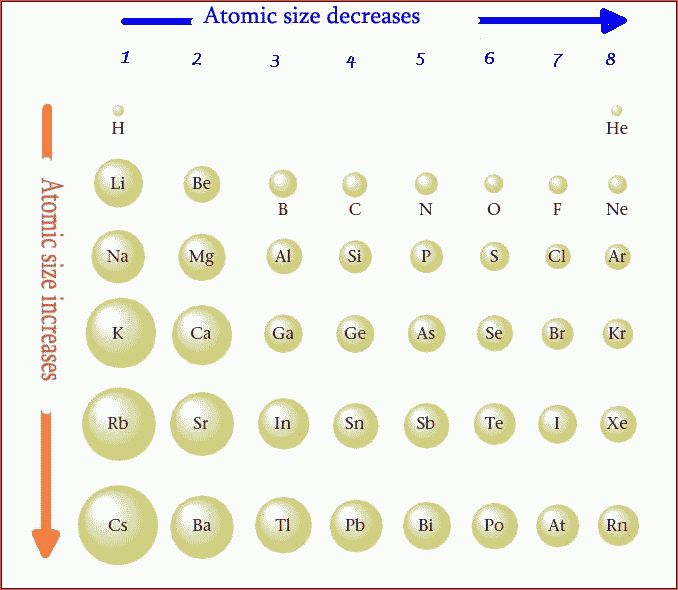
It will also decrease because there are now less electrons in the outer shell, which will decrease the radius size. This will cause a decrease in atomic size because there are now fewer electrons for the protons to pull towards the nucleus and will result in a stronger pull of the electrons towards the nucleus. The loss of an electron means that there are now more protons than electrons in the atom, which is stated above.Which of these elements has the smallest atomic radius Explanation: Helium has the smallest atomic radius. Thus, helium is the smallest element, and francium is the largest. The loss in an electron will consequently result in a change in atomic radii in comparison to the neutral atom of interest (no charge). As can be seen in the figures below, the atomic radius increases from top to bottom in a group, and decreases from left to right across a period.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
